Abstract
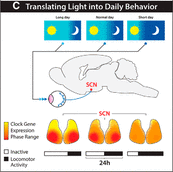
The transcriptional architecture of intracellular circadian clocks is similar across phyla, but in mammals interneuronal mechanisms confer a higher level of circadian integration. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a unique model to study these mechanisms, as it operates as a ∼24 h clock not only in the living animal, but also when isolated in culture. This “clock in a dish” can be used to address fundamental questions, such as how intraneuronal mechanisms are translated by SCN neurons into circuit-level emergent properties and how the circuit decodes, and responds to, light input. This review addresses recent developments in understanding the relationship between electrical activity, [Ca2+]i, and intracellular clocks. Furthermore, optogenetic and chemogenetic approaches to investigate the distinct roles of neurons and glial cells in circuit encoding of circadian time will be discussed, as well as the epigenetic and circuit-level mechanisms that enable the SCN to translate light input into coherent daily rhythms.